Summary
This article explores the major types of modern display technologies—LCD, LED, OLED, AMOLED, Retina Display, IPS, and emerging formats like Mini-LED and Micro-LED. It explains how each technology works, including their light sources, layer structures, advantages, drawbacks, and typical usage in consumer electronics. Each section is accompanied by easy-to-understand 2D and 3D diagrams to illustrate the internal components, helping readers make informed decisions when purchasing devices like smartphones, TVs, or laptops.
Table of Contents
Introduction To Different Display Technology
In today’s digital world, the screen is our window to technology. Whether it’s a smartphone, TV, computer monitor, or smartwatch, display technology plays a vital role in how we interact with digital content. Over the years, display technologies have evolved rapidly to provide better color accuracy, contrast, energy efficiency, and thinner designs. This article delves deep into the most popular types of display technologies: LCD, LED, OLED, AMOLED, Retina Display, and others. We’ll break down how each works, what sets them apart, and where they’re most commonly used.
1. LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
What is LCD?
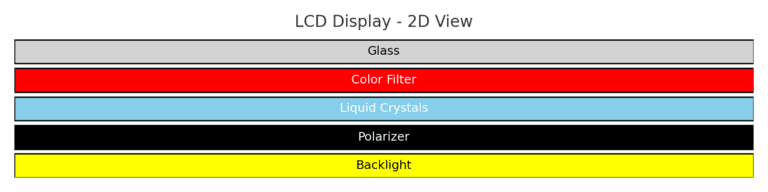
LCDs are among the most widely used display technologies. They consist of liquid crystals sandwiched between two layers of glass and controlled by electric currents to modulate light and produce images.
How It Works:
LCDs do not emit light directly.
A backlight (usually LED) provides illumination.
Liquid crystals twist and align to allow or block light.
A color filter gives the image its colors.
Pros:
Affordable
Widely available
Good brightness in sunlight
Cons:
Limited viewing angles
Lower contrast compared to OLED
Slower refresh rates
Common Uses:
Budget smartphones
TVs
Computer monitors
2. LED (Light Emitting Diode)
What is LED?
An LED display is essentially an LCD screen with LED backlighting instead of older CCFL (cold cathode fluorescent lamp) technology.
How It Works:
Uses LEDs to light the LCD panel.
Improves brightness and contrast.
Offers better energy efficiency than traditional LCDs.
Pros:
Energy-efficient
Slim profile
Improved brightness
Cons:
Still shares LCD limitations (like contrast)
Not self-illuminating like OLED
Common Uses:
LED TVs
Laptops
Monitors
3. OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode)
What is OLED?
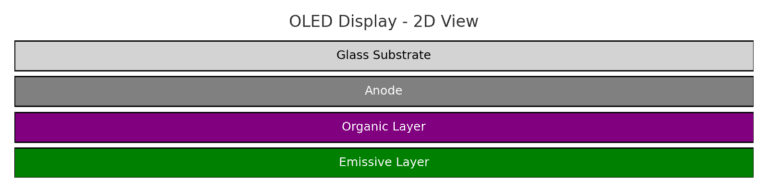
OLED represents a major leap from LCD technology. Each pixel in an OLED display emits its own light, eliminating the need for a backlight.
How It Works:
Organic compounds emit light when electricity passes through.
Individual pixels turn on/off for true blacks and vibrant colors.
Pros:
True blacks
High contrast ratios
Thinner and flexible screens possible
Faster refresh rates
Cons:
Expensive to produce
Risk of burn-in
Shorter lifespan than LCD in some cases
Common Uses:
High-end smartphones
Premium TVs
Wearables
4. AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode)
What is AMOLED?
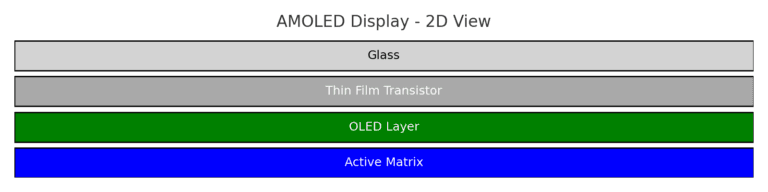
AMOLED is an advanced version of OLED. It integrates an active matrix of thin-film transistors (TFTs) to control each pixel more precisely.
How It Works:
Each pixel is actively controlled with a transistor
Allows for higher refresh rates and better energy efficiency
Great for responsive and touch-integrated displays
Pros:
Deeper blacks and better color reproduction
Better power management than standard OLED
Slim, lightweight
Cons:
Prone to burn-in
Expensive
Common Uses:
Premium smartphones (Samsung Galaxy, OnePlus, etc.)
Smartwatches
5. Retina Display
What is Retina Display?
Coined by Apple, Retina Display isn’t a different technology but a marketing term for screens with a pixel density high enough that individual pixels are not visible to the naked eye at a typical viewing distance.
How It Works:
Often uses IPS LCD or OLED tech underneath
Focus is on pixel density (measured in PPI – pixels per inch)
Diagram:

Pros:
Crisp, clear text and images
Accurate color reproduction
Cons:
More expensive than standard displays
Battery-intensive depending on resolution
Common Uses:
Apple iPhones, iPads, MacBooks
6. IPS (In-Plane Switching) LCD
What is IPS?
IPS is a type of LCD that offers improved viewing angles and color accuracy by rearranging the way liquid crystals are aligned.
How It Works:
Crystals rotate parallel to the screen
Delivers consistent color from all angles
Pros:
Wide viewing angles
Good color accuracy
No ghosting
Cons:
Slower response time
More power consumption than TN (Twisted Nematic) LCDs
Common Uses:
Smartphones
Graphic design monitors
Tablets
7. Mini-LED and Micro-LED (Next-Gen Tech)
What is Mini-LED?
Mini-LED is a refinement of LED backlighting with much smaller LEDs, allowing for more precise local dimming and improved contrast.
What is Micro-LED?
Micro-LED uses microscopic LEDs to form individual pixels, much like OLED, but without organic material—offering better brightness, longevity, and no burn-in.
Pros:
High brightness
Better HDR performance
Long lifespan
Cons:
Expensive
Still evolving
Common Uses:
High-end TVs
Future smartphones
Quick Comparison Table
| Display Type | Light Source | Self-Emissive? | Contrast | Power Efficiency | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCD | Backlight (LED) | No | Moderate | Moderate | Low |
| LED | LED Backlight | No | Better | Better | Low |
| OLED | Each Pixel | Yes | Excellent | High | High |
| AMOLED | Each Pixel + Active Matrix | Yes | Excellent | Very High | High |
| Retina Display | Varies (IPS LCD / OLED) | No/Yes | High | Moderate to High | Medium to High |
| IPS LCD | LED Backlight | No | Good | Moderate | Medium |
| Mini-LED | Advanced LED Backlight | No | Excellent | High | High |
| Micro-LED | Self-Emitting LEDs | Yes | Excellent | Very High | Very High |
Final Thoughts
Understanding the nuances of display technologies can help you make informed decisions whether you’re buying a smartphone, tablet, TV, or monitor. While traditional LCDs and LEDs still dominate many markets due to affordability, OLED and AMOLED offer the best viewing experience today. Apple’s Retina branding emphasizes clarity, while new technologies like Mini-LED and Micro-LED hint at a future of even better display performance.
As display technologies continue to evolve, we can expect even sharper visuals, better energy efficiency, and more immersive experiences across all our digital devices.
Stay tuned to TechMitra.in for more tech breakdowns and expert reviews.
Recent Posts
Ayush Singhal is the founder and chief editor of TechMitra.in — a tech hub dedicated to simplifying gadgets, AI tools, and smart innovations for everyday users. With over 15 years of business experience, a Bachelor of Computer Applications (BCA) degree, and 5 years of hands-on experience running an electronics retail shop, Ayush brings real-world gadget knowledge and a genuine passion for emerging technology.
At TechMitra, he covers everything from AI breakthroughs and gadget reviews to app guides, mobile tips, and digital how-tos. His goal is simple — to make tech easy, useful, and enjoyable for everyone. When he’s not testing the latest devices or exploring AI trends, Ayush spends his time crafting tutorials that help readers make smarter digital choices.
📍 Based in Lucknow, India
💡 Focus Areas: Tech News • AI Tools • Gadgets • Digital How-Tos
📧 Email: contact@techmitra.in
🔗 Full Bio: https://techmitra.in/about-us/
