Switching to solar power is no longer just about saving on electricity bills—it’s about creating a sustainable energy ecosystem where your home or business can produce, consume, and even share electricity with the grid. One of the most widely adopted solutions is the On-Grid Solar Power Plant, also known as a grid-tied solar system.
In this detailed guide, we’ll explore how an on-grid solar power plant works, the role of its components, how it sends power back to the grid, and why it’s the most economical choice for homeowners and businesses.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to On Grid Solar System
An on-grid solar power plant is a solar energy system that is connected directly to the public electricity grid. Unlike off-grid systems, which require expensive batteries for storage, on-grid systems use the grid as a “virtual battery.”
This means you can:
Use solar power during the day to run your appliances.
Send excess electricity back to the grid.
Draw electricity from the grid when solar energy isn’t enough (like at night).
2. Key Components of On-Grid Solar Power Plants
Solar Panels – Convert sunlight into DC electricity.
On-Grid Inverter – Converts DC to AC, synchronizes with the grid.
Net Meter – Records both import and export of electricity.
Distribution Board (DB Box) – Supplies electricity to home appliances.
Utility Grid – Acts as a backup power source and storage system.
3. Step-by-Step Working Process
Step 1: Solar Energy Generation
Solar panels, usually installed on rooftops or open spaces, capture sunlight and generate Direct Current (DC) electricity. The amount of electricity depends on:
Sunlight intensity
Number of solar panels
Efficiency of the panels
Step 2: DC to AC Conversion
Since home appliances and the utility grid run on Alternating Current (AC), the DC electricity from panels is routed to the on-grid inverter, which:
Converts DC → AC
Synchronizes with grid voltage and frequency
Step 3: Powering Your Home
The AC electricity is first supplied to your home’s appliances—lights, fans, refrigerators, computers, TVs, etc. Solar power always takes priority, meaning your home consumes solar energy before using grid power.
Step 4: Exporting Excess Power to the Grid
When your panels generate more electricity than you consume (for example, in the afternoon when you’re not home), the surplus energy flows back into the grid through a net meter.
This process is known as net metering, and you receive credits on your electricity bill for the exported units.
Step 5: Importing Power from the Grid
At night or during cloudy days, when solar production is insufficient, your home automatically imports electricity from the grid. This ensures uninterrupted power supply without the need for batteries.
Also Read : My Solar Rooftop Plant Review (2024-2025)
4. The Role of On Grid Solar Inverter
The on grid Solar inverter is the brain of the system. Its functions include:
Converting DC → AC power.
Synchronizing solar electricity with the grid’s voltage & frequency.
Directing electricity to either your home or the grid.
Preventing power backflow to the grid during outages (safety feature called anti-islanding).
Without the inverter, your solar panels’ electricity would be unusable.
5. Net Metering: How You Save Money
The net meter is a two-way meter that measures both:
Electricity consumed from the grid (imports).
Electricity sent back to the grid (exports).
At the end of the billing cycle, your electricity bill shows the net consumption:
Net Units = Grid Import – Solar Export\text{Net Units = Grid Import – Solar Export}Net Units = Grid Import – Solar Export
If exports exceed imports, you may carry forward credits or even receive payments, depending on local government policies.
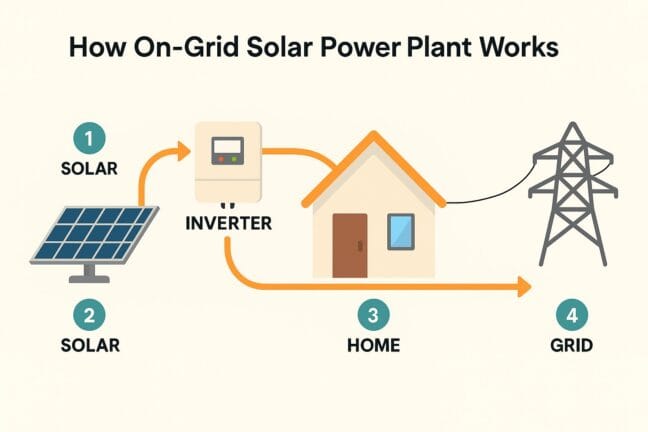
6. Simplified On Grid Solar System Diagram
Here’s a step-by-step visual representation of how an on-grid solar plant works:

Flow:
Solar Panels generate DC electricity.
Inverter converts DC → AC.
Home appliances consume solar power.
Grid receives excess electricity.
7. Advantages of On Grid Solar System Power Plants
Cost-Effective – No need for costly batteries.
Reduced Bills – Significant savings through net metering.
Reliable Power – Grid backup ensures 24×7 electricity.
Environment-Friendly – Reduces carbon footprint.
Income Source – Earn credits for excess energy exported.
Low Maintenance – Few moving parts; only panels need periodic cleaning.
8. Limitations to Consider
No Power During Outages – On-grid systems shut down during blackouts for safety reasons.
Dependent on Net Metering Policies – Savings depend on local government/state regulations.
Requires Good Sunlight – Works best in areas with sufficient solar radiation.
9. Real-Life Example: A Household with On-Grid Solar
Imagine a household with a 5 kW on-grid solar system:
Daily average generation: ~20 units (kWh).
Daily household consumption: 15 units.
Surplus exported: 5 units/day.
At the end of the month:
450 units consumed from solar.
150 units exported to grid.
Grid bill reduced drastically because of net metering credits.
This means the family’s electricity bill almost becomes zero.
10. Conclusion
An On-Grid Solar Power Plant is the smartest and most affordable way to go solar. It allows you to:
Use solar electricity first,
Export surplus energy to the grid, and
Import power when solar is not enough.
The on-grid inverter ensures smooth conversion and synchronization, while net metering policies make the investment highly rewarding.
If you live in an area with a reliable electricity grid and supportive government policies, installing an on-grid solar plant is a win-win solution for your finances and the planet.
Trending
Ayush Singhal is the founder and chief editor of TechMitra.in — a tech hub dedicated to simplifying gadgets, AI tools, and smart innovations for everyday users. With over 15 years of business experience, a Bachelor of Computer Applications (BCA) degree, and 5 years of hands-on experience running an electronics retail shop, Ayush brings real-world gadget knowledge and a genuine passion for emerging technology.
At TechMitra, he covers everything from AI breakthroughs and gadget reviews to app guides, mobile tips, and digital how-tos. His goal is simple — to make tech easy, useful, and enjoyable for everyone. When he’s not testing the latest devices or exploring AI trends, Ayush spends his time crafting tutorials that help readers make smarter digital choices.
📍 Based in Lucknow, India
💡 Focus Areas: Tech News • AI Tools • Gadgets • Digital How-Tos
📧 Email: contact@techmitra.in
🔗 Full Bio: https://techmitra.in/about-us/
